Collapsible content
Description
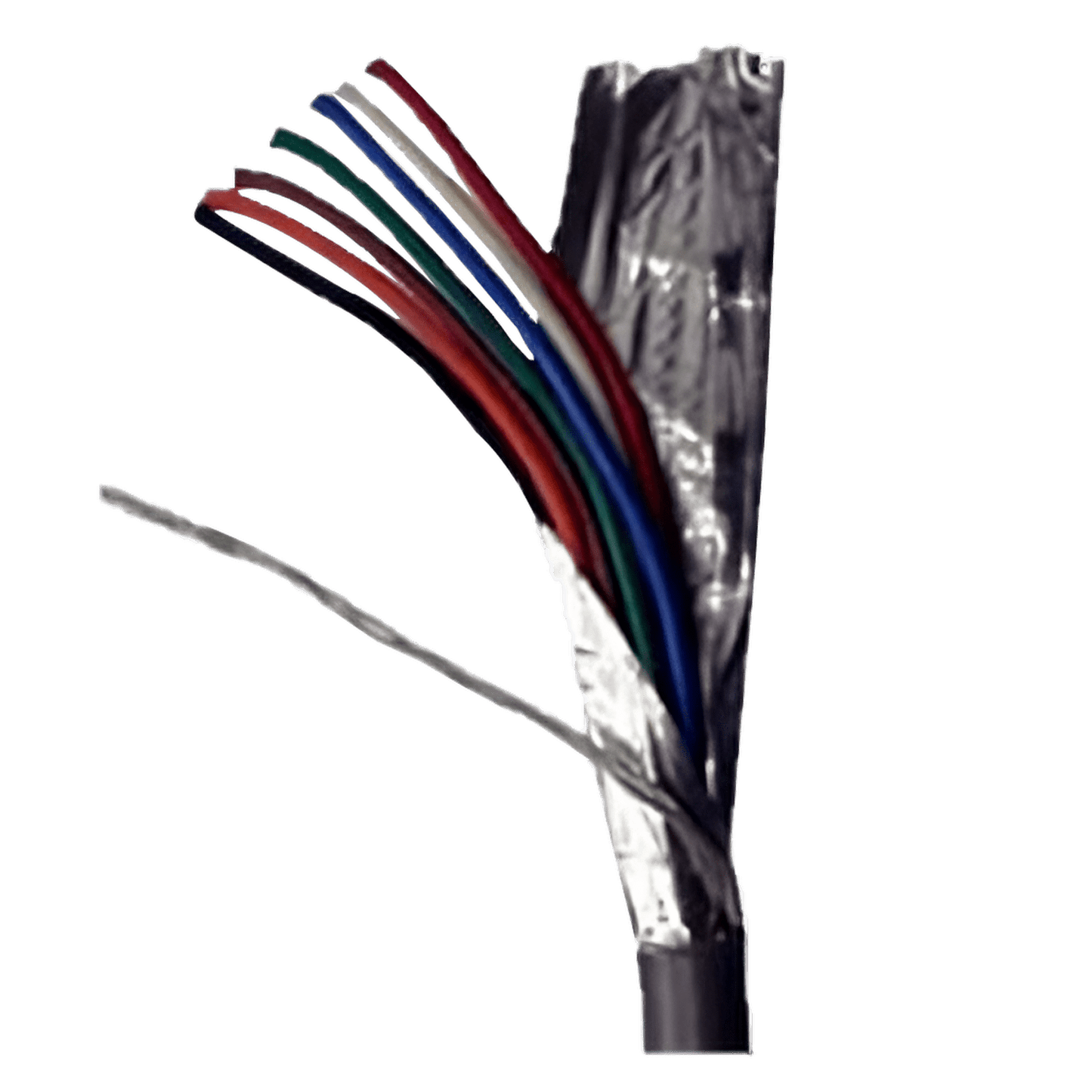
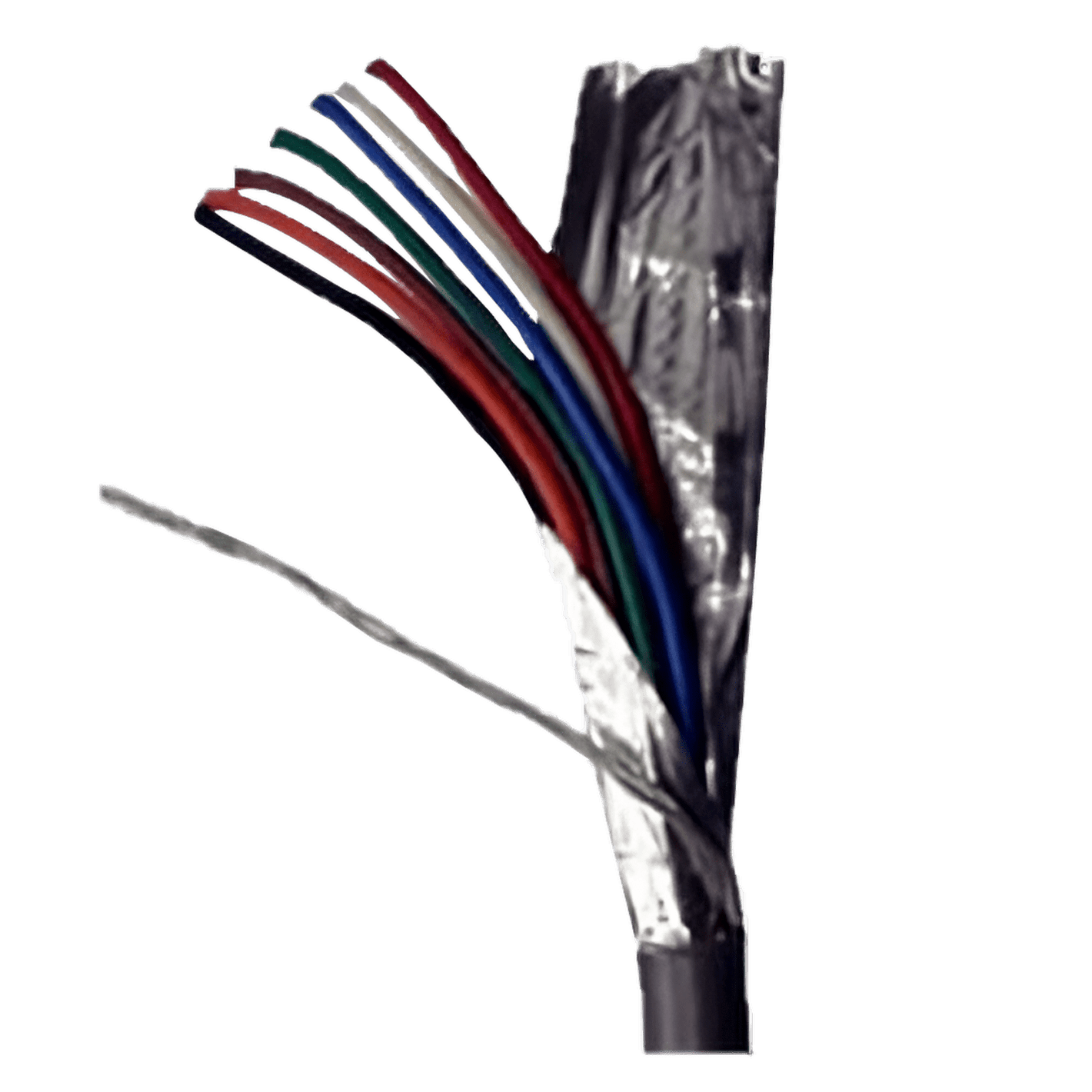
The MaxSonar Connection Wire is used to reduce the interference caused by electrical noise on the lines. This cable is a great solution to use when running the sensors at a long distance or in an area with a lot of EMI and electrical noise. MaxBotix Inc., has successfully tested our sensors at a distance of 1,000 ft using this wire and it was as stable as if it were next to the power supply.
Specs
Documentation and CAD files
Documents
Part Numbers
All MaxBotix part numbers are a combination of a six-character base followed by a dash and a three-digit product code. The following table displays all of the active and valid part numbers for this product.
Active Part Numbers
Product Change Notifications Associated with MB7954 Shielded Cable
No PCNs on Record
Recommended Accessories
-
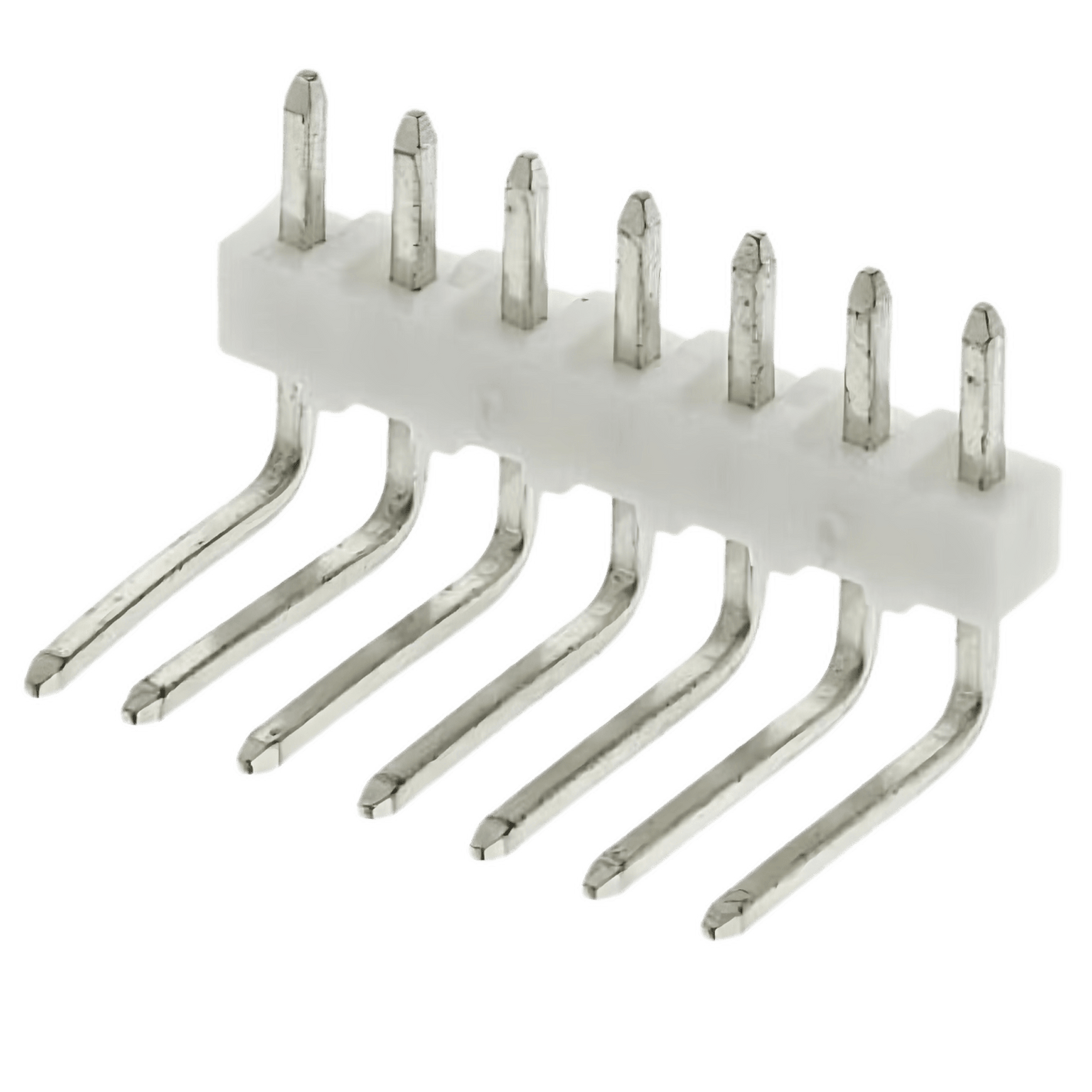
Pin Header (90 Degree 7 Pin) Attached
View AccessoryConnector Header Through Hole, Right Angle 7 position 0.100″ (2.54mm)
-
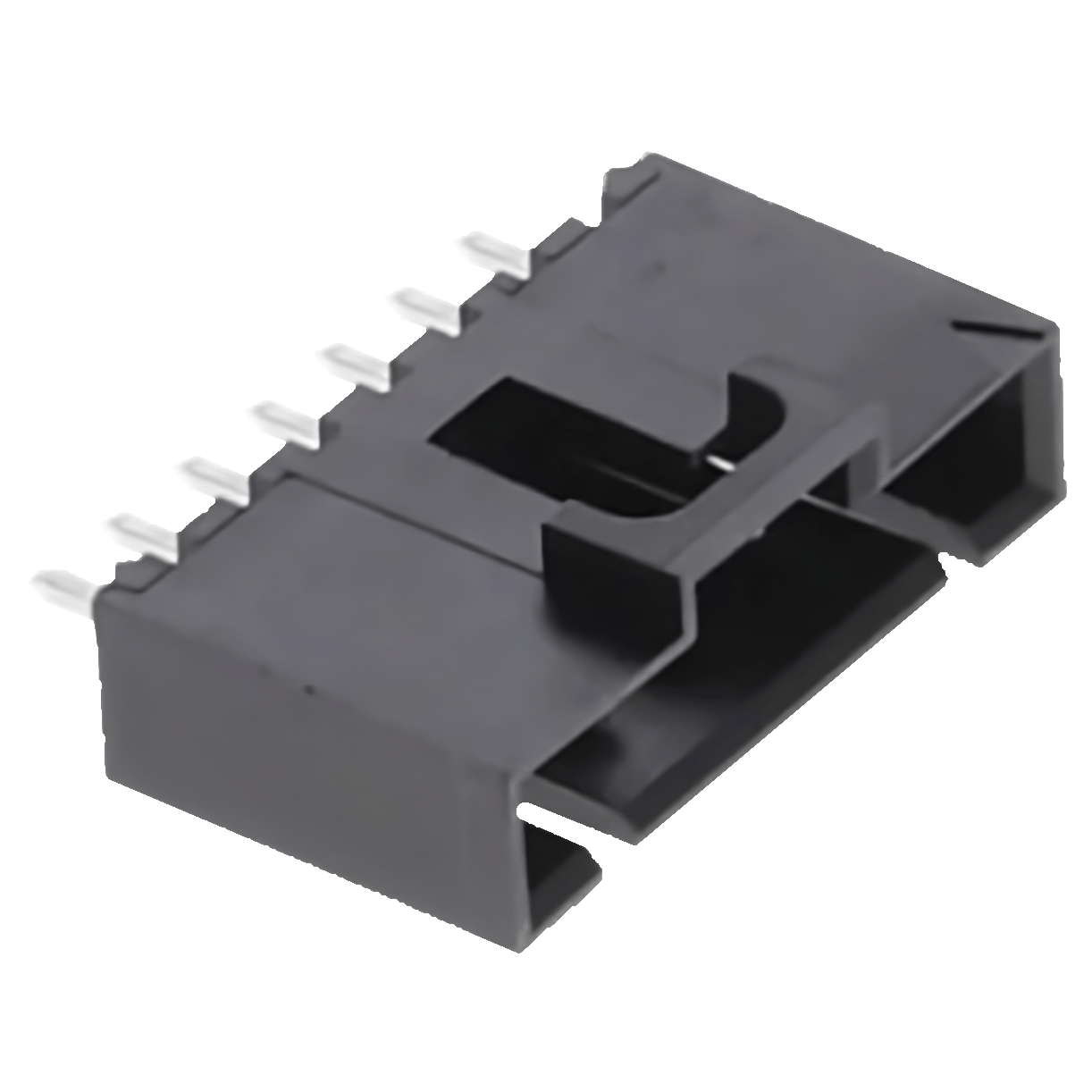
Pin Connector (7 Pin) Attached
View AccessoryConnector Header Through Hole 7 position 0.100″ (2.54mm)
-
Straight 7 Pin Connector Attached
View AccessoryConnector Header Through Hole 7 position 0.100″ (2.54mm)
-

-

-
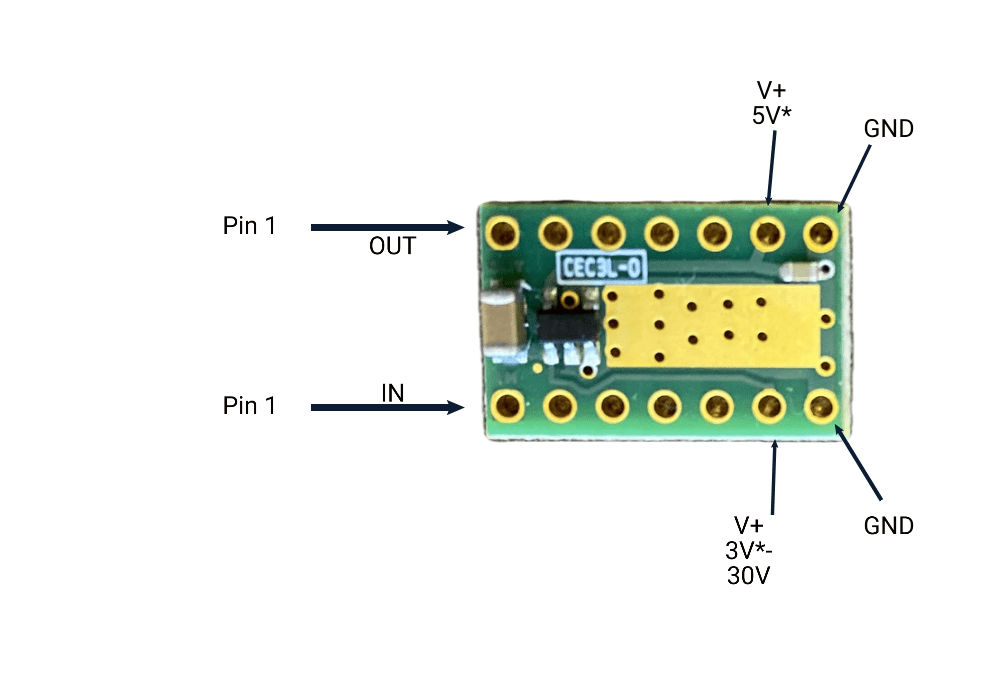
MB7986 Voltage Regulator
View AccessoryThe voltage regulator is used to automatically regulate voltage inputs from 3V to 30V.